Network Security Groups
Rules and Priorities
Service Tags
Virtual Network Service tags | Microsoft doc link
A service tag represents a group of IP address prefixes from a given Azure service. Microsoft manages the address prefixes encompassed by the service tag and automatically updates the service tag as addresses change, minimizing the complexity of frequent updates to network security rules.
Rule Priority
A number between 100 and 4096. Rules are processed in priority order, with lower numbers processed before higher numbers, because lower numbers have higher priority. Once traffic matches a rule, processing stops. As a result, any rules that exist with lower priorities (higher numbers) that have the same attributes as rules with higher priorities aren’t processed.
Inbound Rule Suggestions
Inbound 100 to 109
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 to 109 | 100 to 109 available for overrides | ||||||
Inbound 110 to 199
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | Deny-Internet-to-Any | Any | Any | Internet (Service tag) | Any | Deny | Deny All inbound Internet access. |
| 200 to 299 | Allow any internal vNet services | - | - | - | - | - | Allow any internal vNet services |
Inbound 300
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | Deny-From-VNET-to-VNET | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny | - |
Inbound 301 to 64999
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 301 to 64999 | For non-vnet or internet facing rules | - | - | - | - | - | For non-vnet or internet facing rules |
Inbound 65000 to 65500
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65000 | AllowVnetInBound | Any | Any | VirtualNetwork | VirtualNetwork | Allow | Built in Rule |
| 65000 to 65500 | Are built in rules | - | - | - | - | - | Are built in rules |
Inbound 65500 to 65501
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65500 | AllowAzureLoadBalancerInBound | Any | Any | AzureLoadBalancer | Any | Allow | Built in Rule |
| 65501 | DenyAllInBound | Any | Any | Any | Any | Deny | Built in Rule |
Outbound Rule Suggestings
Outbound 100 to 109
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 to 109 | 100 to 109 available for overrides | ||||||
Outbound 110 to 199
| Priority | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destination | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110 to 199 | Allow any inbound services | Allow any inbound services | |||||
| 111 | Allow http | 80 | TCP | - | Internet (Sevice Tag) | Allow | Allow http services to internet |
| 112 | Allow https | 443 | TCP | - | Internet (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow https services to internet |
| 114 | Allow-DNS-to-MicrosoftAzure | 53 | Any | - | 168.63.129.16 | Allow | Allow DNS to Azure DNS IP |
| 115 | Allow-AADConnect-to-AzureAD | 443,80 | TCP | - | AzureAzureActiveDirectory (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Allow AAD Connect services. |
| 116 | Allow-Azuresiterecovery | 443,80 | TCP | - | AzureSiteRecovery (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Azure Site Recovery services. |
| 117 | Allow-AzureKeyVault | 443,80 | TCP | - | AzureKeyVault (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Azure Key Vault services. (Dependency for ASR). |
| 118 | Allow-GuestAndHybridManagement | 443,80 | TCP | - | GuestAndHybridManagement (Sevice Tag) | Allow | Allow Guest and Hybrid Management services. (Dependency for ASR, AzMonitor). |
| 119 | Allow-Storage | 443,80 | TCP | - | Storage (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Storage services. (Dependency for ASR, AzMonitor). |
| 120 | Allow-EventHub | 443,80 | TCP | - | Eventhub (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Event Hub services. (Dependency for ASR). |
| 121 | Allow-AzureMonitor | 443,80 | TCP | - | AzureMonitor (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Event Hub services. (Dependency for ASR). |
| 122 | Allow-WindowsUpdate-AzUpdateDeliver | 443,80 | TCP | - | AzureUpdateDelivery (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Az update delivery services. |
| 123 | Allow-WindowsUpdate-AzFrontDoorFP | 443,80 | TCP | - | AzureFrontDoor.FirstParty (Service Tag) | Allow | Allow Az update delivery services. |
Flow Logs
NSG flow logs is a feature of Azure Network Watcher that allows you to log information about IP traffic flowing through a network security group (NSG). Flow data is sent to Azure Storage from where you can access it and export it to any visualization tool.
Flow logs for network security groups | Microsoft doc link
Common use cases
All of the below information has been ripped out of a Microsoft doc, not my original material.
Network monitoring
- Identify unknown or undesired traffic.
- Monitor traffic levels and bandwidth consumption.
- Filter flow logs by IP and port to understand application behavior.
- Export flow logs to analytics and visualization tools of your choice to set up monitoring dashboards.
Usage monitoring and optimization
- Identify top talkers in your network.
- Combine with GeoIP data to identify cross-region traffic.
- Understand traffic growth for capacity forecasting.
- Use data to remove overly restrictive traffic rules.
Compliance
- Use flow data to verify network isolation and compliance with enterprise access rules.
- Network forensics and security analysis
- Analyze network flows from compromised IPs and network interfaces.
- Export flow logs to any SIEM or IDS tool of your choice.
Reading the flow log
- Logs are in JSON format and will be outputting in the json file format.
- The information that is interesting is in the flowtuples section of the json file.
Example flow log entry
{
"records": [
{
"time": "2018-11-13T12:00:35.3899262Z",
"systemId": "a0fca5ce-022c-47b1-9735-89943b42f2fa",
"category": "NetworkSecurityGroupFlowEvent",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/RESOURCEGROUPS/FABRIKAMRG/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/NETWORKSECURITYGROUPS/FABRIAKMVM1-NSG",
"operationName": "NetworkSecurityGroupFlowEvents",
"properties": {
"Version": 2,
"flows": [
{
"rule": "DefaultRule_DenyAllInBound",
"flows": [
{
"mac": "000D3AF87856",
"flowTuples": [
"1542110402,94.102.49.190,10.5.16.4,28746,443,U,I,D,B,,,,",
"1542110424,176.119.4.10,10.5.16.4,56509,59336,T,I,D,B,,,,",
"1542110432,167.99.86.8,10.5.16.4,48495,8088,T,I,D,B,,,,"
]
}
]
},
{
"rule": "DefaultRule_AllowInternetOutBound",
"flows": [
{
"mac": "000D3AF87856",
"flowTuples": [
"1542110377,10.5.16.4,13.67.143.118,59831,443,T,O,A,B,,,,",
"1542110379,10.5.16.4,13.67.143.117,59932,443,T,O,A,E,1,66,1,66",
"1542110379,10.5.16.4,13.67.143.115,44931,443,T,O,A,C,30,16978,24,14008",
"1542110406,10.5.16.4,40.71.12.225,59929,443,T,O,A,E,15,8489,12,7054"
]
}
]
}
]
}
},
{
"time": "2018-11-13T12:01:35.3918317Z",
"systemId": "a0fca5ce-022c-47b1-9735-89943b42f2fa",
"category": "NetworkSecurityGroupFlowEvent",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/RESOURCEGROUPS/FABRIKAMRG/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/NETWORKSECURITYGROUPS/FABRIAKMVM1-NSG",
"operationName": "NetworkSecurityGroupFlowEvents",
"properties": {
"Version": 2,
"flows": [
{
"rule": "DefaultRule_DenyAllInBound",
"flows": [
{
"mac": "000D3AF87856",
"flowTuples": [
"1542110437,125.64.94.197,10.5.16.4,59752,18264,T,I,D,B,,,,",
"1542110475,80.211.72.221,10.5.16.4,37433,8088,T,I,D,B,,,,",
"1542110487,46.101.199.124,10.5.16.4,60577,8088,T,I,D,B,,,,",
"1542110490,176.119.4.30,10.5.16.4,57067,52801,T,I,D,B,,,,"
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
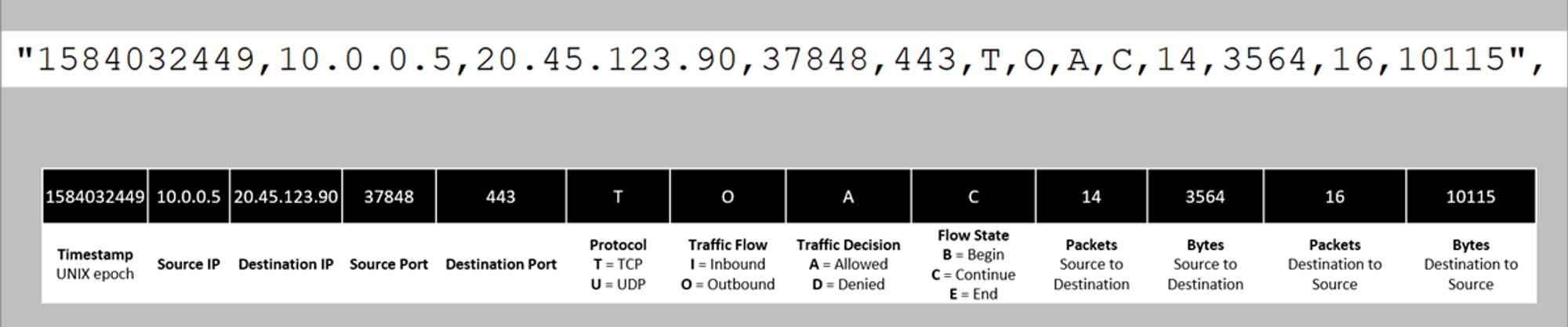
Flow Tuples
flowTuples: String that contains multiple properties for the flow tuple in a comma-separated format
Example entry: 1493695838,185.170.185.105,10.2.0.4,35370,23,T,I,A,C,1021,588096,8005,4610880
Script to read the logs via PowerShell
Dump the below into a file as a script (.ps1) filetype.
To use the script below, navigate to the location of the file, and use the NsgFlowLogFileName switch to select the JSON file.
cd C:\Temp\
.\Parse-NSG-FlowLog_json.ps1 -NsgFlowLogFileName .\PT1H.json | ft -AutoSize
I didn't write this script, I cannot take any credit for it!
param(
[string]$NsgFlowLogFileName = "C:\Temp\filename.json"
)
# Import the logs from the file convert it from json into a powershell object
$logs = gc $NsgFlowLogFileName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | ConvertFrom-Json | select -ExpandProperty records
# Loop through each entry in the json file
foreach ($Log in $Logs)
{
#Get a list of flows
$Flows = $log.properties.flows
# Loop through each flow of each json entry and output the details
foreach ($Flow in $Flows)
{
# Split the flow information to a variable for easier and quicker referencing
$FlowInfo = $Flow.flows.flowtuples[0] -split(',')
# Output details as a powershell object
[pscustomobject]@{
DateTime = (Get-Date 01.01.1970)+([System.TimeSpan]::fromseconds($FlowInfo[0]))
NSGName = $Log.resourceId.split('/')[-1]
RuleName = $Flow.ruleDecision = switch ($FlowInfo[7]) { 'a' { "Allowed" } ; "d" {"Denied"} }
FlowState = switch ($FlowInfo[8]) { 'B' { "Begin" } ; "C" {"Continue"} ; "e" {"End"} }
SourceIP = $FlowInfo[1]
SourcePort = $FlowInfo[3]
DestIP = $FlowInfo[2]
DestPort = $FlowInfo[4]
Protocol = switch ($FlowInfo[5]) { 't' { "TCP" } ; "u" {"UDP"} }
Direction = switch ($FlowInfo[6]) { 'i' { "InBound" } ; "o" {"OutBound"} }
SourcePackets = $FlowInfo[9]
SourceBytes = $FlowInfo[10]
DestPackets = $FlowInfo[11]
DestBytes = $FlowInfo[12]
# Below line ends the flow loop, then filters out the empty entries.
} | where SourceIP -ne $null
}
}